 Introduction
Introduction
Welcome to this comprehensive guide on Human Resource Management.
In this article, we will explore everything from fundamental management concepts to the trends and challenges facing HR professionals today.
Objective of the Article
The aim of this article is to serve as an educational and practical resource for managers, HR professionals, and anyone interested in deepening their knowledge in the field of Human Resource Management.
We will address a variety of topics ranging from basic concepts to advanced metrics, with the intent of offering a 360º view on the subject.
Importance of Human Resource Management Today
Human Resource Management has never been as vital as it is now. Companies of all sizes and sectors face increasing challenges in attracting, retaining, and developing talent.
With digitalization and globalization redefining the work environment, it is imperative for organizations to invest in effective HR strategies to maintain a competitive edge.
In addition, the COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of flexible and resilient HR policies that can adapt to unforeseen circumstances. Human Resource Management has not only become an organizational pillar but also a critical factor for the well-being of employees and the sustainability of the business.
 Basic Concepts and General Definitions
Basic Concepts and General Definitions
Before diving into the details of Human Resource Management, it is crucial to understand some fundamental concepts and definitions that form the foundation of this field. This section will clarify what “management” really means, what “resources” are in an organization, the role of a “manager,” and how “management” differs from “administration.”
What is the concept of management?
Management is the process of planning, organizing, directing, and controlling the resources and activities of an organization, with the aim of achieving specific goals and objectives. In simple terms, management is the art of getting things done through people. It involves effective coordination of resources like time, capital, and workforce to achieve desired results.
What are resources in an organization?
Resources in an organization refer to all the assets used to create value and achieve business objectives. These can be classified into various categories:
| Resource Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Human | Workforce of the organization |
| Financial | Capital, funds, and other forms of financial resources |
| Material | Equipment, raw material, and facilities |
| Information | Data, knowledge, and business intelligence |
What is a manager of a company?
A manager of a company is someone responsible for overseeing and guiding the operations and employees within a department or the entire organization. The role of a manager includes, but is not limited to, strategic planning, decision-making, and problem-solving. The success of a manager is often measured by the effectiveness with which he or she achieves organizational goals, as well as by team satisfaction and productivity.
What is the difference between administration and management?
Although the terms “administration” and “management” are often used interchangeably, they have distinct nuances:
- Administration: Refers more to bureaucratic and operational work, such as completing routine tasks, maintaining records, and implementing policies and procedures.
- Management: Is more focused on making strategic decisions, planning, and leadership. It involves more flexibility and a more dynamic approach to solving complex problems.
To summarize the two concepts briefly: administration is more tactical, management is more strategic.
 Management Functions and Responsibilities
Management Functions and Responsibilities
Understanding the various functions and responsibilities associated with management is vital for the success of any organization. In this section, we will explore the four basic functions of management, the key tasks of the human resources manager, the role of Human Resources itself, and the administrative cycle.
What are the 4 functions of management?
The four fundamental functions of management are Planning, Organizing, Directing, and Controlling. These functions form the backbone of any effective management:
- Planning: Involves setting objectives and choosing the best courses of action to achieve them.
- Organizing: Refers to structuring resources and tasks to achieve the set objectives.
- Directing: Involves leading and motivating the team to execute the plans and tasks.
- Controlling: Involves monitoring performance and taking corrective measures when necessary.
What is human resource management?
Human resource management is a set of practices and strategies aimed at the effective development and administration of an organization’s human capital. This field encompasses a variety of functions and responsibilities ranging from recruitment, selection, and onboarding of new employees, to training, development, and retention of existing talent.
Human resource management is not limited to just administrative aspects like payroll and benefits management. It also encompasses the development of a positive organizational culture, performance evaluation and improvement, promotion of employee engagement and well-being, and the implementation of strategies that align employees’ objectives with those of the organization.
The ultimate goal of human resource management is to maximize the productivity and performance of the organization by optimizing its most valuable resource: people. Learn more here.
What are the key functions and responsibilities of a human resource manager?
The human resource manager has a series of critical functions and responsibilities, which include:
- Recruitment and Selection: Identify and attract talent for the organization.
- Training and Development: Provide growth and learning opportunities for employees.
- Performance Management: Evaluate and improve the effectiveness of employees.
- Compensation and Benefits: Administer salaries, bonuses, and other forms of rewards.
- Labor Relations: Maintain a healthy work environment and resolve conflicts.
What is the role of Human Resources?
The role of Human Resources involves planning, implementing, and managing strategies related to an organization’s human capital. The goal is to maximize employee effectiveness while minimizing associated risks and costs. The Human Resources area also plays a crucial role in organizational culture and employee well-being.
What is the administrative cycle?
The administrative cycle is a continuous process involving the four management functions mentioned earlier: Planning, Organizing, Directing, and Controlling.
This cycle is repeated continuously to ensure that the organization is always moving towards its objectives, adjusting as necessary in response to internal and external changes.
 Skills and Competencies
Skills and Competencies
In this section, we will explore the essential skills and competencies that distinguish an effective human resources manager. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for both those aspiring to enter this field and organizations looking to hire high-performance professionals.
What is the profile of a good human resources manager?
The profile of a good human resources manager is not limited to just technical skills; personal characteristics, or soft skills, also play a vital role.
Some important traits include:
- Integrity: Honesty and ethics in dealing with sensitive issues.
- Flexibility: Adaptability to different situations and challenges.
- Resilience: Ability to maintain focus and calm in high-pressure environments.
- Proactivity: Anticipating and resolving problems before they become critical.
What are the competencies of an HR professional with a strategic vision?
Beyond operational skills, an HR professional with a strategic vision should possess the following competencies:
- Strategic Thinking: Ability to align human resources goals with organizational objectives.
- Change Management: Skill in facilitating and implementing changes effectively.
- Cultural Awareness: Understanding of diverse cultures and business practices.
- Data Analysis: Use of metrics and data to make informed decisions.
What are the skills needed for a human resources manager?
An effective human resources manager should possess a variety of skills, which can be categorized as follows:
| Skill | Description |
|---|---|
| Communication | Ability to convey information clearly and effectively. |
| Leadership | Skill in motivating and guiding the team. |
| Critical Analysis | Aptitude for evaluating situations and making informed decisions. |
| Empathy | Ability to understand and share the feelings of others. |
| Organization | Skill in managing multiple tasks and projects simultaneously. |
 Motivation and Engagement
Motivation and Engagement
Employee motivation and engagement are crucial for the success of any organization. In this section, we will discuss the role of human resources in motivating employees, effective strategies for boosting this motivation, and the key components that make it up.
What is the role of human resources in motivating employees?
The Human Resources department plays a central role in motivating employees. Some of its responsibilities include:
- Recognition and Rewards: Implementing incentive and award systems that recognize merit and performance.
- Professional Development: Offering training opportunities and growth within the organization.
- Employee Well-being: Creating a healthy and inclusive work environment.
- Open Communication: Facilitating communication between management and employees.
What can be done to motivate employees?
Keeping employees motivated requires a multifaceted approach. Some effective strategies may include:
- Clear Goals: Setting clear and achievable objectives to provide direction and purpose.
- Autonomy: Giving employees the freedom to make decisions about their work.
- Constructive Feedback: Providing regular assessments to help employees improve.
- Work-Life Balance: Respecting employees’ personal time to prevent burnout.
What are the three components of job motivation?
Job motivation is often broken down into three main components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Autonomy | The freedom to control one’s own work and make decisions. |
| Competence | The feeling of efficacy and accomplishment in task performance. |
| Relationship | The sense of being connected and valued by others in the organization. |
 Human Capital and Human Resources
Human Capital and Human Resources
In this section, we will discuss the difference between human capital and human resources, the importance of human capital for an organization, and how to effectively capitalize on human resources.
What is the difference between human capital and human resources?
Although the terms “human capital” and “human resources” are often used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings:
- Human Capital: Refers to the set of knowledge, skills, and competencies that employees bring to an organization. It is an intangible asset that can be invested and capitalized on to generate value.
- Human Resources: This term is more comprehensive and includes all aspects related to managing an organization’s personnel, from recruitment to training, compensation, and retention.
What is the importance of human capital?
Human capital is one of the most valuable assets of an organization. Its importance can be highlighted in several ways:
- Innovation: Skilled and experienced employees are the source of innovative ideas.
- Productivity: A high level of human capital generally results in greater efficiency and productivity.
- Competitiveness: Human capital can provide a competitive edge over competitors with a less skilled workforce.
How to capitalize on human resources?
Capitalizing on human resources involves a range of strategies aimed at maximizing the value that employees can bring to the organization:
- Continuous Training: Investing in training programs to enhance the skills of employees.
- Career Development: Providing opportunities for career progression, thus encouraging long-term commitment.
- Recognition and Rewards: Using incentive systems that recognize and reward exceptional performance.
 Challenges and Trends in Human Resources
Challenges and Trends in Human Resources
In this section, we address emerging challenges and trends in Human Resources, providing detailed insights into each crucial area.
Current Challenges in Human Resource Management
The challenges in Human Resource Management are many and varied. Here, we focus on four main areas that are particularly urgent today.
- Diversity and Inclusion Management: Fostering a diverse and inclusive work environment is more than an ethical issue; it is also a competitive advantage. Companies that embrace diversity tend to be more innovative and resilient.
- Remote Work and Flexibility: The pandemic has accelerated the transition to remote work, highlighting the need for flexible work policies, as well as technological tools that allow for distance collaboration.
- Mental Health and Employee Well-being: Employee well-being has a direct impact on productivity and, by extension, on the company’s success. Mental health support programs are increasingly common in organizations.
- Talent Retention: High turnover is costly for any company, both in financial terms and in terms of human capital. Effective retention strategies include professional development programs and competitive benefits.
Emerging Trends
Emerging trends in Human Resources are strongly linked to the rapid evolution of technology and changes in work dynamics.
- Artificial Intelligence and Automation: AI tools are being used to automate repetitive tasks in HR, allowing professionals to focus on more strategic tasks.
- People Analytics: Data analytics in HR is becoming a crucial tool for informed decision-making, from recruiting to employee retention.
- Continuous Learning and Development: As the world of work evolves, so does the need for ongoing professional development. Online courses, webinars, and mentoring programs are on the rise.
- Employer Branding: In a competitive job market, a strong employer brand can be a crucial differentiator for attracting top talent.
Challenges in International Human Resource Management
Managing Human Resources across multiple countries presents a host of unique challenges, from cultural differences to legal issues.
- Cultural Differences: A deep understanding of cultural differences is crucial for effectively managing international teams.
- Global Mobility and International Transfers: Managing expatriate employees and complying with immigration laws are complex aspects of international HR management.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have different labor and tax laws, and it is crucial to be in compliance with all of them to avoid legal sanctions.
The Impact of the Pandemic on Human Resource Management
The pandemic has brought unprecedented challenges but also opportunities to reinvent how we manage Human Resources.
- Adaptation to Remote Work: The pandemic forced many companies to adopt remote work, requiring rapid technological and cultural adaptation.
- Crisis Management and Communication: The health crisis required clear and transparent communication between management and employees, reinforcing the critical role of Human Resources.
- Reassessment of Benefits and Compensation: The pandemic context led many companies to reassess their benefits packages, including mental well-being as a priority.
The Future of Human Resources
The future will bring challenges and opportunities, influenced by both technology and social and demographic changes.
- The growing role of Data Analytics: Data analytics will be increasingly integrated into HR strategies, enabling more effective, data-driven management.
- Ethics and Transparency: Business ethics and transparency will become increasingly important, as employees and the general public demand greater social responsibility from companies.
- Evolution of Workspaces: Workspaces will continue to evolve, with an increasing focus on flexibility, sustainability, and well-being.
Read more in this article: HR Trends: What Will HR Look Like in 2024?
 Indicators and Metrics in Human Resources
Indicators and Metrics in Human Resources
Indicators and metrics in Human Resources are essential tools for evaluating organizational performance and identifying areas for improvement. This section explores the most commonly used types of metrics and how they can be effectively applied.
| Category | Sub-Category | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Performance Indicators (KPIs) | Importance of KPIs | KPIs provide a quantitative basis for measuring the effectiveness of HR strategies. |
| Examples of Common KPIs | Retention rate, employee satisfaction, average time to hire. | |
| Recruitment and Selection Metrics | Time to Hire | Time from job posting to the filling of the position. |
| Cost per Hire | Total cost involved in hiring a new employee. | |
| Quality of Hire | Evaluates the performance of the new employee during the trial period. | |
| Retention and Turnover Metrics | Retention Rate | Percentage of employees who remain in the company for a specified period. |
| Turnover Rate | Percentage of employees who leave the organization during a defined period. | |
| Cost of Turnover | Costs associated with employee departures, such as recruitment and training. | |
| Engagement and Satisfaction Metrics | Engagement Survey | Measures the level of commitment and satisfaction of employees. |
| Employee Net Promoter Score (NPS) | Measures employees’ willingness to recommend the company as a good place to work. | |
| Productivity Metrics | Productivity per Employee | Evaluates the efficiency of each employee. |
| Hours Worked vs. Results | Compares worked hours with achieved results. | |
| Training and Development Metrics | ROI of Training | Measures the effectiveness of training programs in terms of benefits versus costs. |
| Percentage of Employees in Development Programs | Measures the percentage of employees in professional development programs. | |
| Diversity and Inclusion Metrics | Company Demographic Composition | Provides a view of diversity within the organization. |
| Promotion Rates by Demographics | Evaluates promotion rates by demographic group. | |
| Well-Being and Health Metrics | Absenteeism | Refers to the frequency and duration of employee absences. |
| Well-Being Programs | Evaluates the effectiveness of well-being programs on employee health and productivity. |
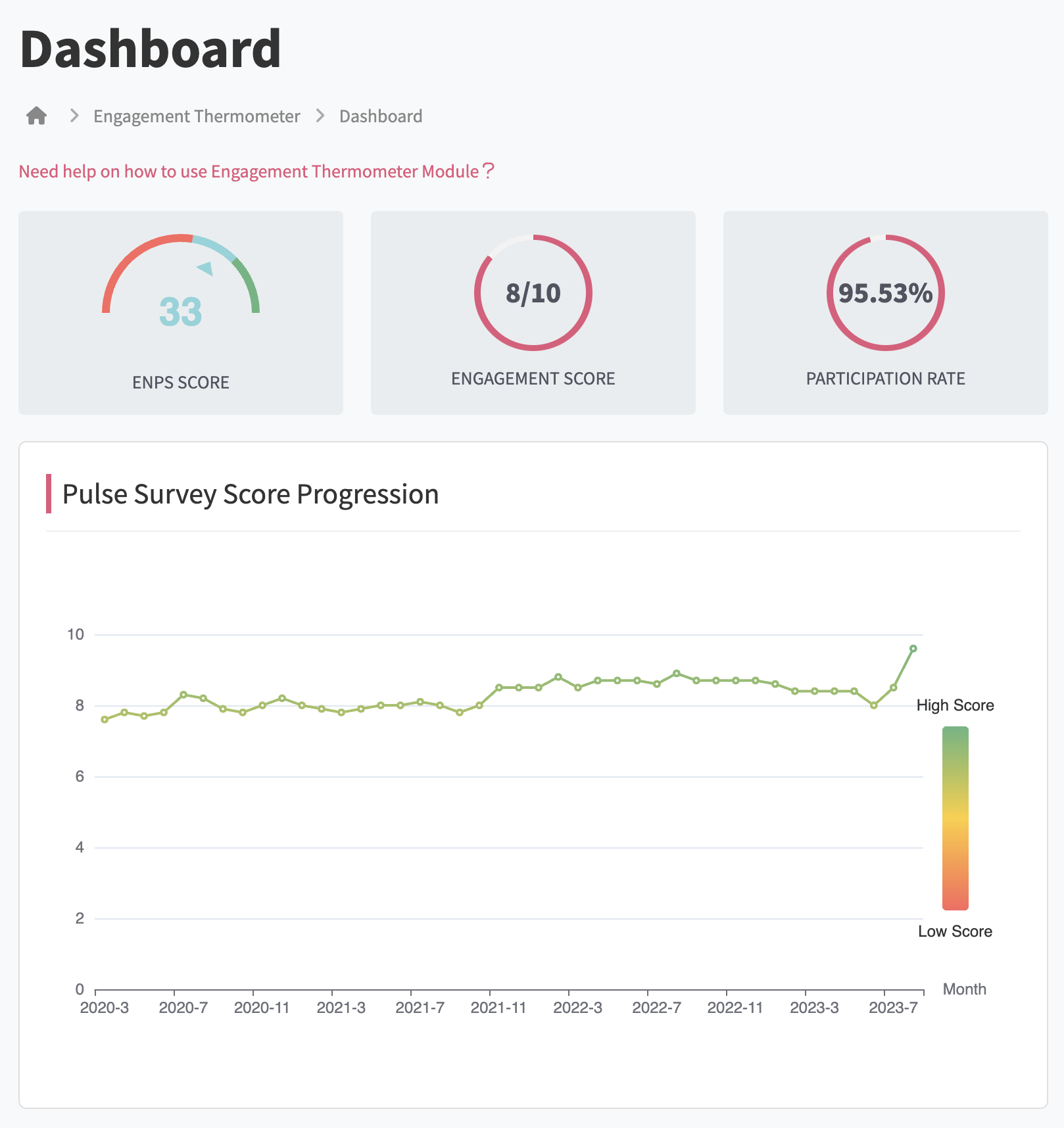
This tool fits perfectly into the modern approach of using data for decision-making in Human Resources. It not only identifies areas that need improvement but also helps validate the impact of new HR policies or initiatives.
This solution aligns with current trends in People Analytics, contributing to more effective and data-based management.
 Development and Learning in Human Resources
Development and Learning in Human Resources
How to Apply People Development in an Organization?
People development is a critical component for the long-term success of any organization. The key is to create an environment that promotes continuous development, both in technical and emotional skills. Mentorship programs, specific workshops, and e-learning platforms are excellent methods for promoting professional development.
Importance of Continuous Training
Continuous training is vital to maintain competitiveness in the market. Besides improving technical skills, it also contributes to employee satisfaction and retention. Online courses, seminars, and conferences are some of the ways to keep the team updated.
Learning and Training Methods
There are various approaches to training and development, each with its own benefits. E-learning offers flexibility, while workshops and hands-on sessions offer more applied learning. The important thing is to use a blended approach to meet different learning needs.
Leadership Development
Effective leaders are crucial for any organization. Leadership development programs, which may include simulations, role-playing games, and 360-degree feedback, can be extremely effective in building stronger leaders.
Performance Evaluation and Feedback
Performance evaluation should not be an annual exercise, but rather a continuous process. Tools like continuous performance reviews and instant feedback can offer valuable insights for individual professional development.
Individual Development Plan (IDP)
The IDP is a personalized plan that identifies the development needs and goals of each employee. Besides being a motivational tool, it also helps managers understand the career paths of their employees.
Development of Social and Emotional Skills
Emotional intelligence has a significant impact on professional success. Programs focusing on the development of social and emotional skills can lead to better working relationships and a healthier work environment.
Return on Investment in Development (ROI)
Evaluating the ROI of development programs is crucial. This not only justifies the costs but also helps improve future programs. ROI should be assessed both in quantitative (costs, participation) and qualitative (satisfaction, retention) terms.
Challenges in Development and Learning
Some of the most common challenges include resistance to change and lack of financial and time resources. However, a well-planned strategy can help overcome these obstacles.
The Future of Development and Learning
With advancements in technology, methods of learning and development are constantly evolving. Virtual reality, artificial intelligence, and other emerging technologies promise to transform the way we approach professional development.
 Digital Platforms and Software in Human Resource Management
Digital Platforms and Software in Human Resource Management
Importance of Digital Platforms and Software
Digital platforms and specialized HR software have transformed the way organizations manage their human capital. From recruitment processes to performance evaluations, digitization has brought efficiency, transparency, and a better experience for employees.
GFoundry is an example of an innovative solution that addresses various needs in Human Resources, from learning and development to evaluation and feedback.
Types of Human Resources Software
There are different types of software to manage various aspects of Human Resources: HR information systems, learning platforms, performance evaluation software, among others. Each offers specific functionalities that meet different organizational needs.
| Type of Software | Description |
|---|---|
| Human Resources Information Systems (HRIS) | Comprehensive systems that cover multiple HR functions, from personnel management and payroll to recruitment and performance evaluation. |
| Talent Management Software | Focuses on recruitment, onboarding, performance management, and succession planning. |
| Learning and Development Platforms (LMS) | Help to administer, track, and deliver training or development courses and programs. |
| Performance Evaluation Software | Provides functionalities for performance evaluations, peer reviews, and continuous feedback. |
| Benefits Management Software | Helps companies manage and track employee benefits like health insurance, pension plans, and others. |
| Time and Attendance Management System | Tracks working hours, absences, and leaves, facilitating payroll management. |
| Employee Engagement Software | Aims to increase employee satisfaction and retention through engagement surveys, feedbacks, and recognition. |
| Onboarding Software | Helps to integrate new employees, providing resources like onboarding checklists, introductions, and initial training. |
| Recruitment and Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) | Assist in job posting, candidate filtering, and interview process management. |
| HR Analytics and Reporting Solutions | Provide detailed analytics and reports on various HR metrics, aiding in data-driven decision-making. |
| Employee Experience Software | These systems focus on creating a positive work experience for employees, covering from onboarding to development and well-being in the work environment. |
Current Trends
Artificial intelligence, data analytics, and gamification are some of the trends shaping the HR world. GFoundry, for example, uses gamification and AI to increase employee engagement, aligning with the latest trends. Read more: HR Trends: What Will HR Look Like in 2024?
Choosing the Right Software
Choosing the right software depends on several factors like the size of the company, specific HR needs, and available budget. GFoundry offers a scalable and customizable solution that can be adapted to meet a variety of business needs.
Integration with Other Systems
The ability to integrate with other systems is crucial to maximize efficiency. GFoundry allows integrations with ERP systems, communication platforms, and others, facilitating more cohesive management. Read more here about GFoundry integrations with other platforms.
Use Cases and Case Studies
Case studies can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of an HR software. GFoundry has been used in various industries to improve employee engagement, talent management, and organizational effectiveness. Learn about case studies in various contexts and industries here.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While digital platforms bring numerous benefits, they also raise ethical issues, such as data privacy. It is crucial to choose platforms that comply with regulations and best practices in information security.
The Future of Digital Platforms in HR
The future is promising with the advent of technologies like AI, machine learning, and blockchain. Platforms like GFoundry are at the forefront of this revolution, offering solutions that not only solve current challenges but are also adaptable to future needs. Read more: A Comprehensive Guide to the Impact, Benefits, and Future of Artificial Intelligence in HR.
The Importance of Artificial Intelligence in Human Resources Management: The Role of Gi, GFoundry’s AI Assistant
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing human resources management, enabling a more personalized and efficient approach to employee training and development.
Gi, GFoundry’s AI assistant, plays a crucial role in this context by creating personalized educational materials and predicting trends like employee turnover. Integrated into the GFoundry platform, Gi offers smarter talent management, helping companies maximize their employees’ potential through advanced AI solutions. Click here to learn more.

Subscribe to GFoundry Newsletter: Weekly Insights on HR’s Most Pressing Topics
Keep on Reading:
- Preparing for the Future of Work: Trends in Job Market 2030
- Mastering Employee Turnover: The Ultimate Guide to Retaining Talent and Boosting Productivity
- The Ultimate Guide for Remote Onboarding
- A Comprehensive Guide to the Impact, Benefits, and Future of Artificial Intelligence in HR
- HR Trends: What Will HR Look Like in 2024?
- Benefits of a Good Organizational Climate: Productivity and Talent Retention
- Building Resilient and Adaptive Workforces: A Global Talent Trends Study
- Employee Feedback: complete guide with real examples
- How to improve Employee Engagement and Performance? Your Ultimate Guide
Ready to get started?
Take the next step and learn more about how GFoundry can help you.
 Introduction
Introduction Basic Concepts and General Definitions
Basic Concepts and General Definitions Management Functions and Responsibilities
Management Functions and Responsibilities Skills and Competencies
Skills and Competencies Motivation and Engagement
Motivation and Engagement Human Capital and Human Resources
Human Capital and Human Resources Challenges and Trends in Human Resources
Challenges and Trends in Human Resources Indicators and Metrics in Human Resources
Indicators and Metrics in Human Resources Development and Learning in Human Resources
Development and Learning in Human Resources Digital Platforms and Software in Human Resource Management
Digital Platforms and Software in Human Resource Management